Benutzer-Werkzeuge
Seitenleiste
techniken:metalldetektor
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Metalldetektor
Für eine vollständige Beschreibung sowie den Originalcode besucht diese Website.
Theorie
Mithilfe eines Metalldetektors ist es möglich, zu bestimmen, ob ein Objekt aus Metall besteht, bzw. um Metall zu detektieren. Der Detektor besteht hauptsächlich aus einer Spule, deren Induktivität durch das in der Nähe befindliche Metall verändert wird. Diese Änderung wird durch den Arduino gemessen und es kann festgestellt werden, ob sich Metall in der Nähe des Messaufbaus befindet.
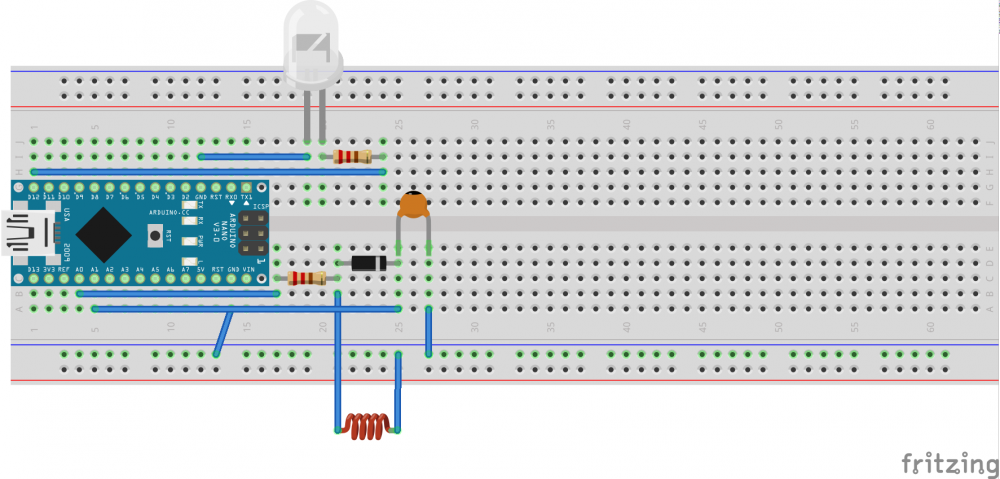
Schaltplan
Bauteile:
1 Arduino Nano
1 10 nF Kondensator
1 Diode
2 220 Ohm Widerstand
1 LED
etwa 5 Meter dünnes Kabel zu einer Spule gewickelt
Code
/* * Metal detector * We use the code of this project, * with minor changes: * https://www.instructables.com/id/Simple-Arduino-Metal-Detector/ */ const byte npulse = 3; // number of pulses to charge the capacitor before each measurement const byte pin_pulse = A0; // sends pulses to charge the capacitor (can be a digital pin) const byte pin_cap = A1; // measures the capacitor charge const byte pin_LED = 12; // LED that turns on when metal is detected void setup() { pinMode(pin_pulse, OUTPUT); digitalWrite(pin_pulse, LOW); pinMode(pin_cap, INPUT); pinMode(pin_LED, OUTPUT); digitalWrite(pin_LED, LOW); } const int nmeas = 256; //measurements to take long int sumsum = 0; //running sum of 64 sums long int skip = 0; //number of skipped sums long int diff = 0; //difference between sum and avgsum long int flash_period = 0; //period (in ms) long unsigned int prev_flash = 0; //time stamp of previous flash void loop() { int minval = 1023; int maxval = 0; //perform measurement long unsigned int sum = 0; for (int imeas = 0; imeas < nmeas + 2; imeas++) { //reset the capacitor pinMode(pin_cap, OUTPUT); digitalWrite(pin_cap, LOW); delayMicroseconds(20); pinMode(pin_cap, INPUT); //apply pulses for (int ipulse = 0; ipulse < npulse; ipulse++) { digitalWrite(pin_pulse, HIGH); //takes 3.5 microseconds delayMicroseconds(3); digitalWrite(pin_pulse, LOW); //takes 3.5 microseconds delayMicroseconds(3); } //read the charge on the capacitor int val = analogRead(pin_cap); //takes 13x8=104 microseconds minval = min(val, minval); maxval = max(val, maxval); sum += val; //determine if LEDs should be on or off long unsigned int timestamp = millis(); byte ledstat = 0; if (timestamp < prev_flash + 10) { if (diff > 0)ledstat = 1; if (diff < 0)ledstat = 2; } if (timestamp > prev_flash + flash_period) { if (diff > 0)ledstat = 1; if (diff < 0)ledstat = 2; prev_flash = timestamp; } if (flash_period > 1000)ledstat = 0; //switch the LEDs to this setting if (ledstat == 0) { digitalWrite(pin_LED, LOW); } if (ledstat == 1) { digitalWrite(pin_LED, LOW); } if (ledstat == 2) { digitalWrite(pin_LED, HIGH); } } //subtract minimum and maximum value to remove spikes sum -= minval; sum -= maxval; //process if (sumsum == 0) sumsum = sum << 6; //set sumsum to expected value long int avgsum = (sumsum + 32) >> 6; diff = sum - avgsum; if (abs(diff)<avgsum >> 10) { //adjust for small changes sumsum = sumsum + sum - avgsum; skip = 0; } else { skip++; } if (skip > 64) { // break off in case of prolonged skipping sumsum = sum << 6; skip = 0; } // one permille change = 2 ticks/s if (diff == 0) flash_period = 1000000; else flash_period = avgsum / (2 * abs(diff)); }
techniken/metalldetektor.txt · Zuletzt geändert: 2019/02/19 17:37 von d.golovko